Hubble Watches Spun-Up Asteroid Coming Apart
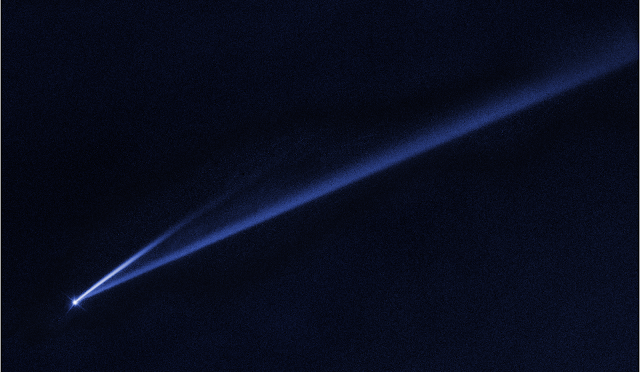 |
| Hubble image of asteroid (6478) Gault |
A small asteroid has been caught in the process of spinning so fast it’s throwing off material, according to new data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and other observatories.
Images from Hubble show two narrow, comet-like tails of dusty debris streaming from the asteroid (6478) Gault. Each tail represents an episode in which the asteroid gently shed its material—key evidence that Gault is beginning to come apart.
Discovered in 1988, the 2.5-mile-wide (4-kilometer-wide) asteroid has been observed repeatedly, but the debris tails are the first evidence of disintegration. Gault is located 214 million miles (344 million kilometers) from the Sun. Of the roughly 800,000 known asteroids between Mars and Jupiter, astronomers estimate that this type of event in the asteroid belt is rare, occurring roughly once a year.
Watching an asteroid become unglued gives astronomers the opportunity to study the makeup of these space rocks without sending a spacecraft to sample them.
This Hubble Space Telescope image reveals the gradual self-destruction of an asteroid, whose ejected dusty material has formed two long, thin, comet-like tails. The longer tail stretches more than 500,000 miles (800,000 kilometers) and is roughly 3,000 miles (4,800 kilometers) wide. The shorter tail is about a quarter as long. The streamers will eventually disperse into space.
When sunlight heats an asteroid, infrared radiation escaping from its warmed surface carries off angular momentum as well as heat. This process creates a tiny torque that can cause the asteroid to continually spin faster. When the resulting centrifugal force starts to overcome gravity, the asteroid’s surface becomes unstable, and landslides may send dust and rubble drifting into space at a couple miles per hour, or the speed of a strolling human. The researchers estimate that Gault could have been slowly spinning up for more than 100 million years.
Piecing together Gault’s recent activity is an astronomical forensics investigation involving telescopes and astronomers around the world. All-sky surveys, ground-based telescopes, and space-based facilities like the Hubble Space Telescope pooled their efforts to make this discovery possible.
“Gault is the best ‘smoking gun’ example of a fast rotator right at the two-hour limit,” said team member Jan Kleyna of the University of Hawaii in Honolulu.
An analysis of the asteroid’s surrounding environment by Hubble revealed no signs of more widely distributed debris, which rules out the possibility of a collision with another asteroid causing the outbursts.
The asteroid’s narrow streamers suggest that the dust was released in short bursts, lasting anywhere from a few hours to a few days. These sudden events puffed away enough debris to make a “dirt ball” approximately 500 feet (150 meters) across if compacted together. The tails will begin fading away in a few months as the dust disperses into interplanetary space.
Based on observations by the Canada–France–Hawaii Telescope, the astronomers estimate that the longer tail stretches over half a million miles (800,000 kilometers) and is roughly 3,000 miles (4,800 kilometers) wide. The shorter tail is about a quarter as long.
Only a couple of dozen active asteroids have been found so far. Astronomers may now have the capability to detect many more of them because of the enhanced survey capabilities of observatories such as Pan-STARRS and ATLAS, which scan the entire sky. “Asteroids such as Gault cannot escape detection anymore,” Hainaut said. “That means that all these asteroids that start misbehaving get caught.”
The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and ESA (European Space Agency). NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C.
For more information about 6478 Gault and Hubble, visit:
http://hubblesite.org/news_release/news/2019-22
Credits: NASA, ESA, K. Meech and J. Kleyna (University of Hawaii), and O. Hainaut (European Southern Observatory)
Release Date: March 28, 2019
#NASA #Space #Astronomy #Hubble #SolarSystem #Asteroid #Asteroid6478 #Gault #Mars #Jupiter #Sun #Telescope #ESO #Observatory #Europe #ESA #Goddard #GSFC #STScI #Exploration #UnitedStates #STEM #Education
No comments:
Post a Comment